bar graph A graph in which information is represented using bars of various lengths to show values of a particular category.
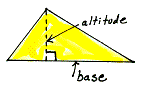
base Given 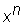 , or x^n, the "x" is the base. The base number gets multiplied by itself the number of times indicated by the exponent, "n".
, or x^n, the "x" is the base. The base number gets multiplied by itself the number of times indicated by the exponent, "n".
Ex:
2^3 = 2x2x2.
base angles of an isosceles triangle Two angles of an isosceles triangle whose vertices are the endpoints of the base of the triangle.
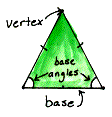 | The base angles on an isosceles triangle are congruent. |
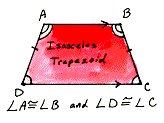 | The base angles on an isosceles trapezoid are congruent. In this example, angles A and B are congruent base angles as are angles D and C. |
betweenness of numbers A number is between two others if it is greater than one of them and less than the other.
betweenness of points A point is between two other points on the same line if its coordinate is between their coordinates.
biconditional statement A statement that includes a conditional and its converse. It may be written in the form p=>q and q=>p, or p<=>q, or "p if and only if q."
Ex:
It is raining if and only if drops of water are falling from the sky.
This statement is a biconditional because it is true when read front to back and also when it is read back to front, its converse;
Drops of water are falling from the sky if and only if it is raining.
A good definition consists of a true conditional and its converse, which also must be true. So biconditional statements are important to find.
bilateral symmetry A space figure has bilateral symmetry if and only if there is a plane over which the reflection image of the figure is the figure itself.
Ex:
x+2
x^2 - 4
3x^2y + 7x
bisector A point, line, ray, or plane which divides a segment, angle,or figure into two parts of equal measure.
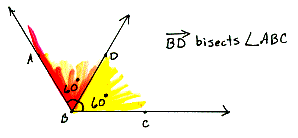
bisector of an angle The ray in the interior of an angle that divides the angle into two angles of equal measures.

 Labels:
Math terms glossary
Labels:
Math terms glossary

 Previous Article
Previous Article
