capacity The number of unit cubes or parts of unit cubes that can be fit into a solid. Also called volume.
cartesian plane Name given to the plane containing points identified as ordered pairs of real numbers. Also called coordinate plane.

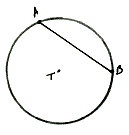
center of a circle The given point from which the set of points of the circle are all at the same distance.
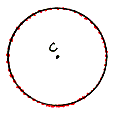 | Every point on this circle is the same distance away from the center point,"C". |
center of a sphere The given point from which the set of points of the sphere are all the same distance.
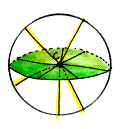 | Every point on this sphere is the same distance away from its center point, "C". |
center of symmetry For a rotation-symmetric figure, the center of a rotation that maps the figure onto itself.
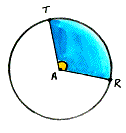 | Angle A is a central angle of this circle because its vertex is the center point "A". |
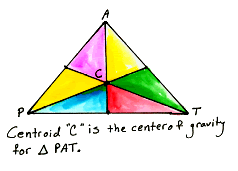 | The median is a segment that connects a vertex with the midpoint of the opposite side. When you draw all these medians, they will intersect at the centroid. The centroid is also the center of gravity. So any triangle will balance perfectly on the tip of a pin at its centroid point. Give it a try. It's really cool. |
 | NOTE: It's important to remember that a circle is only the points on the border. Any point on the inside of this border is in the interior of the circle and is part of what we call the circular region. |
circle graph A graph in which information is represented using a circle that is cut into sectors to show values of a particular category. Also called a pie graph.
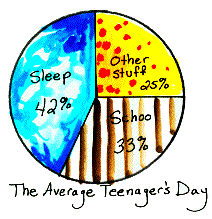
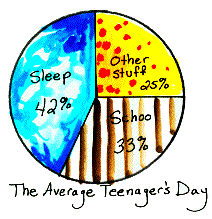
circularity The "circling back" that sometimes occurs when one tries to define basic terms; returning to the word which one is trying to define.
circumference The perimeter of a circle, which is found by multiplying its diameter times pi.
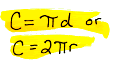
circumscribed circle A circle that is drawn around the outside of a triangle and contains all the vertices of the triangle. A circle is circumscribed about a polygon if each vertex of the polygon lies on the circle.
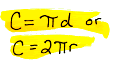
circumscribed circle A circle that is drawn around the outside of a triangle and contains all the vertices of the triangle. A circle is circumscribed about a polygon if each vertex of the polygon lies on the circle.

clockwise rotation The direction in which the hands move on a nondigital clock, designated by a negative magnitude.
Ex: 3xy (the 3 is the coefficient)
coincident lines Lines that contain exactly the same points. We like to think that they lie on top of each other.
Ex:
Given 1/2, 1/3, 1/4 one common denominator would be 12,
because 2, 3, & 4 all divide into 12 evenly.
24, 36, 48 etc. would also be common denominators but 12 is used most often because it is the smallest, or "least common denominator", and thus is easier to work with.
Commutative Property of Addition For any numbers a and b:
a+ b = b + a. Notice the positions of the numbers switch, but the quantities are still equal.
a+ b = b + a. Notice the positions of the numbers switch, but the quantities are still equal.
Ex:
3 +4 = 4 + 3
7=7
Commutative Property of Multiplication For any numbers a and b:
ab = ba. Notice the positions of the numbers switch, but the quantities are still equal.
ab = ba. Notice the positions of the numbers switch, but the quantities are still equal.
Ex:
5 x 6 = 6 x 5
30 = 30
composite number Any positive integer exactly divisible by one or more positive integers other than itself and 1.
Ex:
6 is a composite number because 2 & 3 divide it evenly as well as do 6 & 1.
conclusion The "then" clause of a condition. The result of a deduction in a proof. Also called consequent.
Ex:
If a quadrilateral has four equal sides then it is a rhombus.
congruence transformation A transformation that is a reflection or composite of reflections; also called an isometry.
congruent figures Figures with the same size and shape. Figures which are the image of each other under a reflection, rotation, or translation, or combination of these.
conic solid The set of points between a given region (its base), together with the vertex and the base.
construction A drawing which is made using only an unmarked straightedge and a compass following certain prescribed rules.
contrapositive A conditional resulting from negating and switching the antecedent and consequent of the original conditional.
convenient location A general location for a figure on a coordinate plane in which its key points are described with the fewest possible variables.
converse The conditional statement formed by switching the antecedent and consequent of a given conditional.
coordinate The number or numbers associated with the location of a point on a line, a plane, or in space.
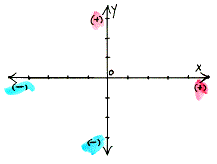
coordinate axes A pair of perpendicular coordinatized lines in a plane that intersect at the point with coordinate 0; three mutually perpendicular coordinatized lines in space that are concurrent at the point with coordinate 0.
 |  |
coordinate plane Name given to the plane containing points identified as ordered pairs of real numbers. Also called cartesian plane.


coordinatized line A line on which every point is identified with exactly one number and every number is identified with a point on the line.
corresponding angles Any pair of angles in similar locations in relation to a transversal intersecting two lines.
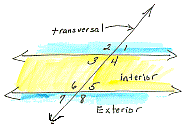 | In this example we see four sets of corresponding angles. 1&5, 2&6, 3&7, 4&8 If the lines cut by the transversal are parallel, all correspondig angles will be congruent. |
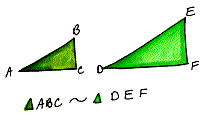 | Ex: The segment stretching from A to B correspondS to the segment stretching from D to E. |
cosine of an angle The ratio leg adjacent to the angle divided by the hypotenuse in a right triangle. Abbreviated cos.


counterclockwise The direction around a circle opposite from that in which the hands of a clock move.


counterclockwise orientation The orientation "walking" around a figure keeping its interior to the left.
counterclockwise rotation The direction opposite that which the hands move on a nondigital clock, designated by a positive magnitude.
counterexample A specific case of a conditional for which the antecedent is true but the consequent is false. An example which shows a conjecture to be false.
counting unit The name of the particular things being tallied in a count.
Ex: I have 5 dollars. ( The count is 5, and the counting unit is dollars.)
Ex: I have 5 dollars. ( The count is 5, and the counting unit is dollars.)
cube root A real number x is the cube root of a real number y, written
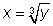 , if and only if x cubed= y. ex:
, if and only if x cubed= y. ex: 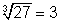
 Labels:
Math terms glossary
Labels:
Math terms glossary




 Previous Article
Previous Article
