decimal notation The notation in which numbers are written using ten digits and each place stands for a power of ten.
Ex: 34 means 3 tens and 4 ones.
Remember that a fraction is a division problem. The top number, the numerator, is the number being divided, the fraction bar is the division symbol, and the bottom number, the denominator, is the number of equal parts that you are dividing the top into.
EX: Say you have $24/8. Twenty four dollars divided into 8 equal parts means there will be $3 in each part.
EX: If the fraction has a numerator smaller than its denominator you might get a problem like this: $3/4. Three dollars divided into 4 equal parts. Each of these parts will have less than one dollar in it, in this case $.75.
*If the numerator is greater than the denominator, the fraction is > 1.
**If the numerator is less than the denominator, the fraction is < 1.
dense The property that between two elements of the set there is at least one other element of the set.
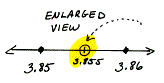 | The set of Real Numbers is dense because between any two numbers you can always find another number, just enlarge the view. |
diagonal of a polygon A segment that connects two vertices of the polygon but is not a side of a polygon.
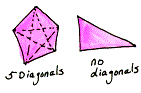 | NOTE: A triangle has no diagonals. |
diameter of a circle or sphere A segment connecting two points on the circle or sphere and containing the center of the circle or sphere, also the length of that segment.
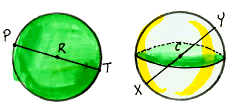
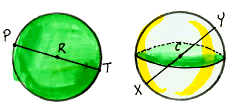
dimensions The lengths of the sides of a rectangle. The number of rows and the number of columns in a rectangular array.
dimensions of a box The lengths of three edges of the box which meet at the same vertex. Usually referred to as length, width, and height.
dimensions of a rectangle The lengths of two sides of the rectangle which meet at a single vertex. Usually referred to as length and width.
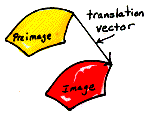
direction of translation The direction given by the vector from any preimage point to its image point in a translation.

discrete geometry The study of points as dots separate from each other, and lines made up of these points.
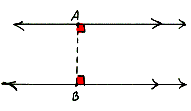
distance between two parallel lines The length of a segment that is perpendicular to the lines with an endpoint on each of the lines.

distance between two parallel planes The length of a segment perpendicular to the planes with an endpoint in each plane.
distance between two points The absolute value of the difference of their coordinates on a coordinatized line.
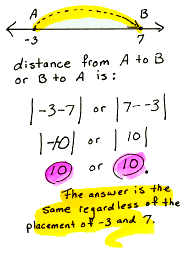
distance from a point to a line The length of the perpendicular segment connecting the point to the line.
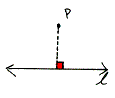
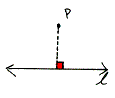
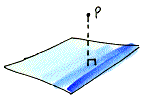
distance from a point to a plane The length of the perpendicular segment from the point to the plane.

Distributive Property of Multiplication over Addition For any numbers a, b, and x : ax + bx = ( a + b )x and x( a + b) = xa + xb. Also called distributivity.
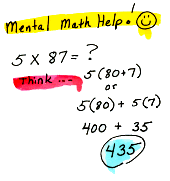
Distributive Property of Multiplication over Subtraction For any numbers a, b, and x : ax + bx = ( a - b )x and ( a - b ) = ax - bx. Also called distributivity.
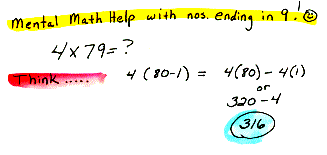
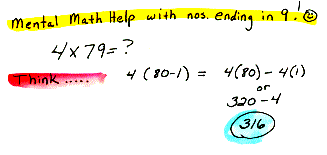
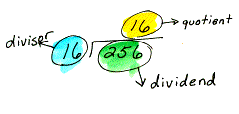
divisor The number by which you divide in a quotient; b is the divisor in a/b. Also a number that exactly divides into another number, referred to as a factor.
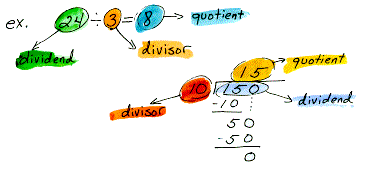
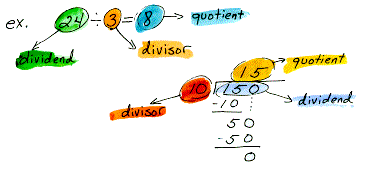
 Labels:
Math terms glossary
Labels:
Math terms glossary

 Previous Article
Previous Article
