if and only if statement A statement consisting of a conditional and its converse. Also called biconditional.
EX:
A quadrilateral is a square if and only if it is a rhombus and a rectangle.
EX:
A quadrilateral is a square if and only if it is a rhombus and a rectangle.
NOTE: The if and only if part , sometimes abbreviated as iff, guarantees that the statement can be read as an "if then" statement from front to back and from back to front, known as the converse. This is how the above example would read in both directions:
Front to back: If a quadrilateral is a square, then it is a rhombus and a rectangle.
Back to front: If a quadrilateral is a rhombus and a rectangle, then it is a square.
if-then statement A statement of the form If... Then....
Ex:
If a quadrilateral has four equal sides then it is a rhombus.
Ex:
If a quadrilateral has four equal sides then it is a rhombus.
image The result of applying a transformation to an original figure or preimage. Transformations can be reflections, as seen in the example below, rotations, translations or "slides", and glide reflections.
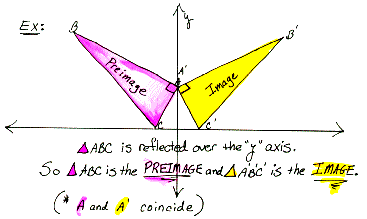

image point A point resulting from applying a transformation. In the example above, C', read "C prime", is the image point of preimage point C.
inch ( in) The base unit of length for the US system of measurement.
1 in is exactly equal to 2.54 centimeters.
1 in is exactly equal to 2.54 centimeters.
indirect reasoning (proofs) Reasoning (proofs) using the Law of the Contrapositive, the Law of Ruling Out Possibilities, or the Law of Indirect Reasoning.
<(less than),
>(greater than),
<(less than or equal to),
>(greater than or equal to).
infinite decimal A decimal that goes on forever to the right of the decimal point. Some of these decimals repeat and some do not. The ones which do not are called irrational numbers examples of which are pi and the square root of two.
infinite repeating decimal A decimal in which a digit or group of digits to the right of the decimal point repeats forever.
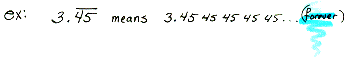
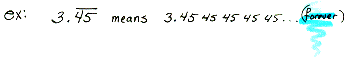
inscribed angle in a circle An angle whose vertex is on the circle and whose sides each intersect the circle at a point other than the vertex.
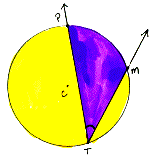 | Angle PTM is an inscribed angle with its vertex point T on the circle C. Notice both sides cross the circle at points other than T. |
 | Here we see a circle that fits perfectly inside of a polygon. The circle ever so lightly touches each side of the polygon, but does not go past its edges. |
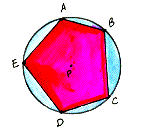 | Notice the difference here. In this case, the polygon is inside the circle with each of its vertices on the circle. |
instance An example of a pattern.
EX:
3x+7 is the pattern and 3(1)+7 = 10 is an instance of that pattern.
EX:
3x+7 is the pattern and 3(1)+7 = 10 is an instance of that pattern.
instance of a conditional A specific case in which the antecedent (if part) of the conditional is true and its consequent (then part) is also true.
EX:
If x is not equal to zero, then x squared is a positive number. An instance here would be let x=(-14), then (-14) squared is equal to 196 which is a positive number.
EX:
If x is not equal to zero, then x squared is a positive number. An instance here would be let x=(-14), then (-14) squared is equal to 196 which is a positive number.
interior angles When two lines are cut by a transversal, the angles that are formed on the inside of the two lines are known as interior angles.
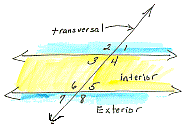 | In this picture, angles 3, 4, 5, and 6 are all interior angles. Angles 1, 2, 7, and 8 are called exterior angles. |
interior of a circle The set of points at a distance less than the radius from the center of the circle. It's all of the points on the inside of the circle.
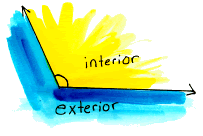
interior of an angle A nonzero angle separates the plane into two sets of points. If the angle is not straight, the convex set is the interior of the angle.

international system of measurement A system of measurements based on the decimal system. Also called metric system.
intersection of two sets The set of elements which are in both the sets.
EX:
Given set A={1, 2, 3, 4} and set B={3, 4, 5, 6},
the intersection of sets A and B, written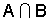 = {3, 4}.
= {3, 4}.
EX:
Given set A={1, 2, 3, 4} and set B={3, 4, 5, 6},
the intersection of sets A and B, written
inverse A conditional resulting from negating the antecedent and consequent of the original conditional.
EX:
EX:
Original conditional: If a quadrilateral is a square, then it is a rectangle.
Inverse: If a quadrilateral is not a square, then it is not a rectangle.
NOTE: Sometimes the original conditional will be true, but its inverse will be false. Be careful with these.
irrational number A number that cannot be written as a simple fraction. It is an infinite and nonrepeating decimal. Examples are "pi" and the square root of two.
isometry A transformation that is a reflection or a composite of reflections. Also called congruence transformation or distance-preserving transformation. Reflections, rotations, translations or slides, and glide reflections are all isometries.
 Labels:
Math terms glossary
Labels:
Math terms glossary

 Previous Article
Previous Article
