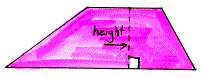
height In a triangle or trapezoid, the segment from a vertex perpendicular to the line containing the opposite side; also, the length of that segment. In a prism or cylinder, the distance between the bases. In a pyramid or cone, the length of a segment from the vertex perpendicular to the plane of the base. Also called altitude.
height of a triangle The perpendicular distance from any vertex of a triangle to the side opposite that vertex. Also called altitude.


hemisphere The half of a sphere on one side of a great circle.
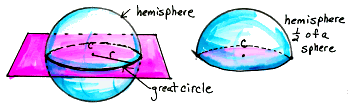
*Remember that a great circle is the intersection of a sphere and a plane that contains the center of the sphere.

*Remember that a great circle is the intersection of a sphere and a plane that contains the center of the sphere.
hidden lines Lines in a picture or a three-dimensional figure that cannot be seen, but which are marked as dashed or shaded lines so as to show existence or give a feeling of depth.
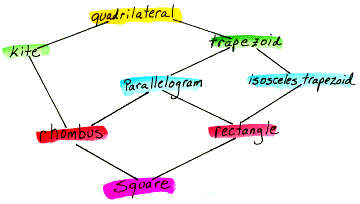
hierarchy A diagram that shows how various figures or ideas are related, often with a down ward direction that moves from more general to more specific. Below you will see the seven types of quadrilaterals arranged in a hierarchy. A hierarchy is similar to a flowchart.

horizontal component of a vector The first component in the ordered pair description of a vector, indicating its magnitude along the x-axis of the coordinate plane.
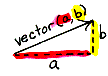 | When a figure is translated on the coordinate plane by a vector (a,b), the image of the point (x,y) is (x+a,y+b). In other words, you add "a" to the first coordinates and "b" to the second coordinates. |
horizontal line A line with an equation y = k on the coordinate plane. No matter what value "x" may assume, the "y" value for every point on this line is locked at the value "k".
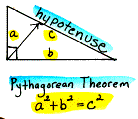
hypothesis The "if" clause of a conditional, also called the antecedent. An assumption used as the basis for an investigation or argument.
Ex: If "x" is a positive number, then "x" is not equal to zero. (*The green part is the hypothesis)
 Labels:
Math terms glossary
Labels:
Math terms glossary


 Previous Article
Previous Article
